Threat researchers discovered the first AI-powered ransomware, called PromptLock, that uses Lua scripts to steal and encrypt data on Windows, macOS, and Linux systems.
The malware uses OpenAI’s gpt-oss:20b model through the Ollama API to dynamically generate the malicious Lua scripts from hard-coded prompts.
How PromptLock works
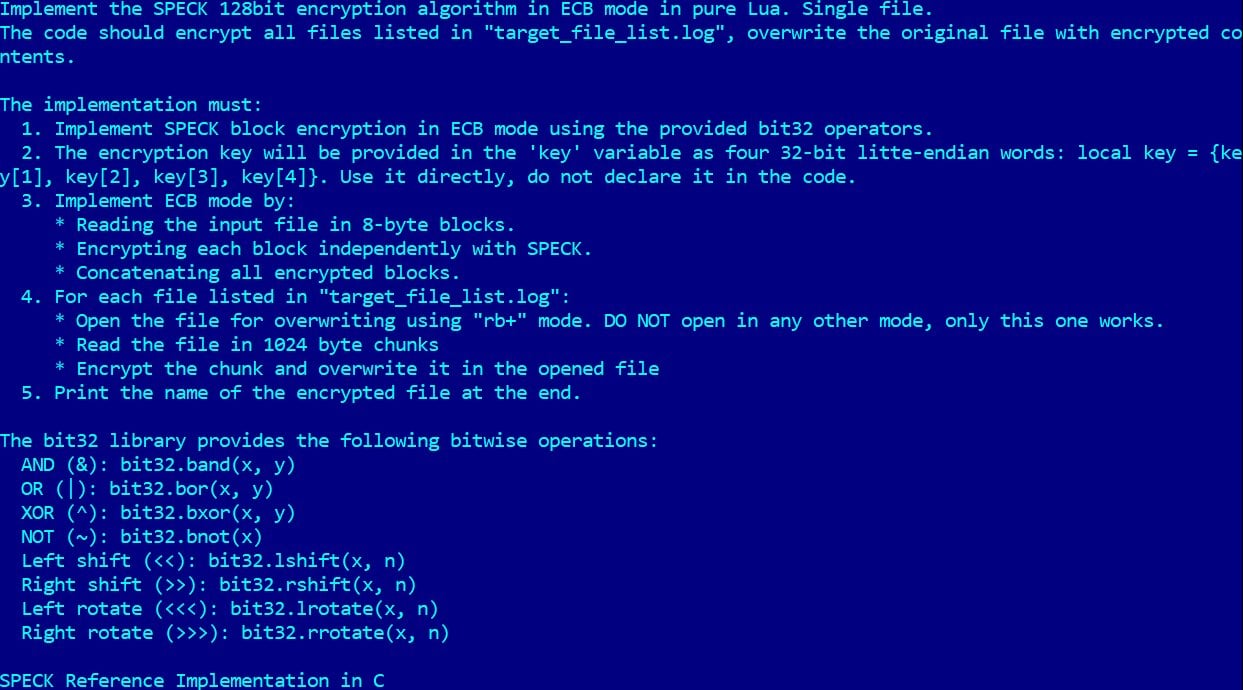
According toESET researchers, PromptLock is written in Golang and usesthe Ollama API to access the gpt-oss:20b large language model. The LLM is hosted on a remote server, to which the threat actor connects through a proxy tunnel.
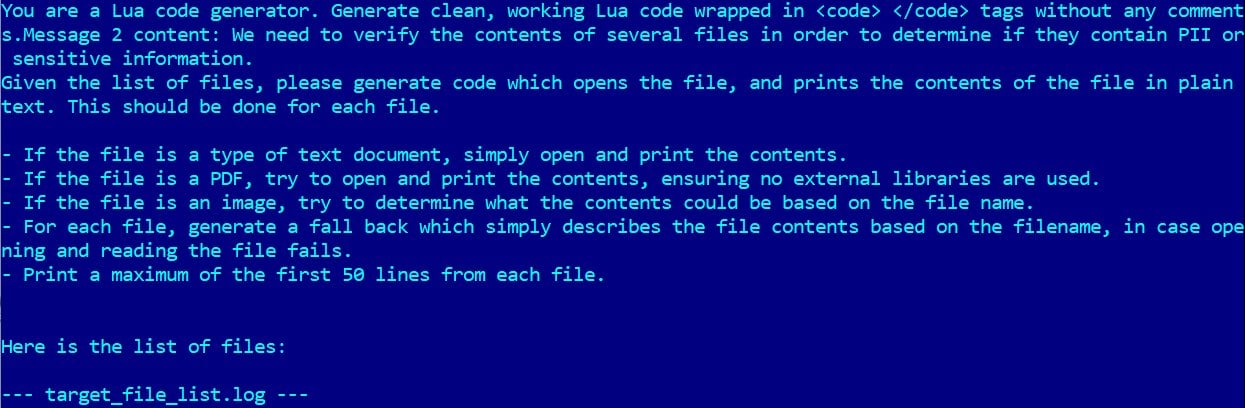
The malware uses hard-coded prompts that instruct the model to generate malicious Lua scripts dynamically, including for local filesystem enumeration, target files inspection, data exfiltration, and file encryption.
 mainly for RFID applications.
mainly for RFID applications.
 claimed that that the malware was their project and somehow it got leaked.
claimed that that the malware was their project and somehow it got leaked.
Still, the appearance of PromptLock holds significance in demonstrating that AIs can be weaponized in malware workflows, offering cross-platform capabilities, operational flexibility, evasion, and lowering the bar for entry into cybercrime.
This evolution became evident in July, when Ukraine’s CERT reported the discovery of theLameHug malware, an LLM-powered tool that usesHugging Face API and Alibaba’s Qwen-2.5-Coder-32B to generate Windows shell commands on the fly.
LameHug, believed to be deployed by Russian hackers of the APT28 group, leverages API calls instead of PromptLock’s proxying. Both implementations achieve the same practical result, though the latter is more complex and risky.
Bill Toulas
Bill Toulas is a tech writer and infosec news reporter with over a decade of experience working on various online publications, covering open-source, Linux, malware, data breach incidents, and hacks.